Posted: June 9th, 2008 | Author: xanda | Filed under: Ads, IT Related | Tags: MSI, msi vr320, msi vr320x, ubuntu, ubuntu 8.04, vr320, vr320x | 6 Comments »

[image source: MSI]
This tutorial can also be used for computers with the following spec:
- Realtek High Definition Audio
- RT61 or RT2500 Wireless Cards
Ok.. lets start..
- Download the installation CD. (see GettingUbuntu)
- Burn the ISO to a CD (see BurningIsoHowto) and check to make sure it was burned correctly. (see Installation/CDIntegrityCheck)
- Proceed with normal installation of Ubuntu by booting from the installation CD. (see GraphicalInstall)
- Once the installation is finish, reboot your machine and boot into your fresh Ubuntu 8.04
- Run update and upgrade
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade |
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
- Add the Medibuntu repo as well 😉
sudo wget http://www.medibuntu.org/sources.list.d/hardy.list -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/medibuntu.list |
sudo wget http://www.medibuntu.org/sources.list.d/hardy.list -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/medibuntu.list
- Now run apt-get update and install the medibuntu keyring
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install medibuntu-keyring && sudo apt-get update |
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install medibuntu-keyring && sudo apt-get update
- As i mentioned in my previous post, Ubuntu 8.04 contains several problems especially when it is running on my notebook. Some of the problems are looping sound and unsupported wifi card. To avoid these, you can use i386 kernel and so far all the problems are no longer appear. To install the i386 kernel, run the following command
sudo apt-get install linux-headers-386 linux-image-386 linux-386 |
sudo apt-get install linux-headers-386 linux-image-386 linux-386
- Now your need to reboot and boot into the i386 kernel
- Lets install several packages
sudo apt-get install envyng-gtk audacious vlc mplayer mozilla-mplayer w32codecs flashplugin-nonfree libflashsupport gstreamer0.10-ffmpeg gstreamer0.10-pitfdll gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad-multiverse gstreamer0.10-plugins-ugly gstreamer0.10-plugins-ugly-multiverse libavcodec1d libavformat1d libavutil1d libcdaudio1 libdc1394-13 libdvdread3 libfaac0 libfaad0 libgmyth0 libgsm1 libiptcdata0 liblame0 libmjpegtools0c2a libmpeg2-4 libmysqlclient15off libopenspc0 libpostproc1d libquicktime1 libsidplay1 libsoundtouch1c2 libwildmidi0 libx264-57 libxvidcore4 msttcorefonts unrar sun-java6-jre sun-java6-plugin |
sudo apt-get install envyng-gtk audacious vlc mplayer mozilla-mplayer w32codecs flashplugin-nonfree libflashsupport gstreamer0.10-ffmpeg gstreamer0.10-pitfdll gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad-multiverse gstreamer0.10-plugins-ugly gstreamer0.10-plugins-ugly-multiverse libavcodec1d libavformat1d libavutil1d libcdaudio1 libdc1394-13 libdvdread3 libfaac0 libfaad0 libgmyth0 libgsm1 libiptcdata0 liblame0 libmjpegtools0c2a libmpeg2-4 libmysqlclient15off libopenspc0 libpostproc1d libquicktime1 libsidplay1 libsoundtouch1c2 libwildmidi0 libx264-57 libxvidcore4 msttcorefonts unrar sun-java6-jre sun-java6-plugin
- MSI VR320 or 320X is using ATI graphics card, so you need to install the ATI driver. Since EnvyNG has been install in previous step, now you just need to run EnvyNG
Applications > System Tools > EnvyNG
Once EnvyNG is loaded, just simply click Apply and wait for the installation to finish. After that reboot your machine
- Apply THIS, THIS, THIS, THIS and THIS tweak
- Done!
Q: I think my fresh installation is fine on my spec. Why it is different on your spec?
A: Ubuntu 8.04 is a mistake!
Posted: May 25th, 2008 | Author: xanda | Filed under: IT Related | Tags: howto, ubtunu 8.04, xmms | 49 Comments »
After Gentoo and Slackware, now is the time for Ubuntu removing XMMS packages from their repo. How SAD! And for those who still want XMMS installed in their Ubuntu, here is the tip.
This this is originally written by Sartek and modified by me
Update your packages list
Now install build-essential
sudo apt-get install build-essential |
sudo apt-get install build-essential
Alright, now we need to install the XMMS’s dependencies
sudo apt-get install autotools-dev automake1.9 libtool gettext libasound2-dev libaudiofile-dev libgl1-mesa-dev libglib1.2-dev libgtk1.2-dev libesd0-dev libice-dev libmikmod2-dev libogg-dev libsm-dev libvorbis-dev libxxf86vm-dev libxml-dev libssl-dev |
sudo apt-get install autotools-dev automake1.9 libtool gettext libasound2-dev libaudiofile-dev libgl1-mesa-dev libglib1.2-dev libgtk1.2-dev libesd0-dev libice-dev libmikmod2-dev libogg-dev libsm-dev libvorbis-dev libxxf86vm-dev libxml-dev libssl-dev
Now create a working directory and change into that directory
Download XMMS sources:
wget http://xmms.org/files/1.2.x/xmms-1.2.11.tar.gz |
wget http://xmms.org/files/1.2.x/xmms-1.2.11.tar.gz
Extract the file and enter the extracted directory
tar xvf xmms-1.2.11.tar.gz
cd xmms-1.2.11/ |
tar xvf xmms-1.2.11.tar.gz
cd xmms-1.2.11/
Run configure with –prefix=/usr
./configure --prefix=/usr |
./configure --prefix=/usr
In my case (Intel Pentium Core Duo), I’ve enable CFLAGS options for processor optimization
CFLAGS="-march=prescott -O2 -pipe -fomit-frame-pointer" ./configure --prefix=/usr --enable-gnutls=yes |
CFLAGS="-march=prescott -O2 -pipe -fomit-frame-pointer" ./configure --prefix=/usr --enable-gnutls=yes
You can simply use the command without the CFLAGS above, or if you want to optimize the pidgin to suit your processor, you can refer to Safe_Cflags page (Gentoo.. uhukk..)
Now compile it and install it
Now lets create the shortcut in your Gnome Menu
Right click on your Gnome Menu, and click on Edit Menu and follow these pictures:
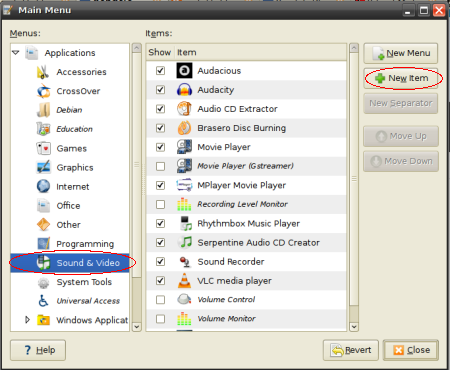

Finish! now just simply remove your build (working) directory
Haih… Event XMMS is not in the repo… seriously Ubuntu 8.04 is a mistake!
Posted: May 17th, 2008 | Author: xanda | Filed under: IT Related | Tags: bandwidth, linux, optimize, tcp, tweak | 6 Comments »
Simply modify your sysctl file and poof!
sudo gedit /etc/sysctl.conf |
sudo gedit /etc/sysctl.conf
copy and past the following code at the last line on your sysctl file
# increase TCP max buffer size setable using setsockopt()
net.core.rmem_max = 16777216
net.core.wmem_max = 16777216
# increase Linux autotuning TCP buffer limits
# min, default, and max number of bytes to use
# set max to at least 4MB, or higher if you use very high BDP paths
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 16777216
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 65536 16777216
# don't cache ssthresh from previous connection
net.ipv4.tcp_no_metrics_save = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_moderate_rcvbuf = 1
# recommended to increase this for 1000 BT or higher
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 2500
# for 10 GigE, use this, uncomment below
# net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 30000
# Turn off timestamps if you're on a gigabit or very busy network
# Having it off is one less thing the IP stack needs to work on
#net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0
# disable tcp selective acknowledgements.
net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 0
#enable window scaling
net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1 |
# increase TCP max buffer size setable using setsockopt()
net.core.rmem_max = 16777216
net.core.wmem_max = 16777216
# increase Linux autotuning TCP buffer limits
# min, default, and max number of bytes to use
# set max to at least 4MB, or higher if you use very high BDP paths
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 16777216
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 65536 16777216
# don't cache ssthresh from previous connection
net.ipv4.tcp_no_metrics_save = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_moderate_rcvbuf = 1
# recommended to increase this for 1000 BT or higher
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 2500
# for 10 GigE, use this, uncomment below
# net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 30000
# Turn off timestamps if you're on a gigabit or very busy network
# Having it off is one less thing the IP stack needs to work on
#net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0
# disable tcp selective acknowledgements.
net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 0
#enable window scaling
net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1
tada… now run the following command
Posted: May 10th, 2008 | Author: xanda | Filed under: IT Related | Tags: active sync, linux, sync, sync in linux, ubuntu, wm5, wm6 | 12 Comments »
“ActiveSync is a synchronisation program developed by Microsoft. It allows a mobile device to be synchronized with either a desktop PC, or a server running Microsoft Exchange Server, PostPath Email and Collaboration Server, Kerio MailServer, Zimbra or Z-Push.” (Wikipedia, 2008)
But how to synchronize your Windows Mobile device in Linux? The solution for ActiveSync alternative on Linux is SynCE. The purpose of the SynCE project is to provide a means of communication with a Windows Mobile device from a computer running Linux, *BSD or other unixes using USB or Bluetooth. One can then use one’s computer to browse files, install applications and synchronize contacts, calendar and tasks with their PIM application of choice.
Lets setup it on our machine. This tutorial is working on Ubuntu 8.04 (Hardy).
First add SynCE repository to your sources.list
echo "deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/synce/ubuntu hardy main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list
echo "deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/synce/ubuntu hardy main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list |
echo "deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/synce/ubuntu hardy main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list
echo "deb-src http://ppa.launchpad.net/synce/ubuntu hardy main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list
Now update your packages list
As i mention before, Ubuntu 8.04 is a mistake. Ubuntu generic kernel might have some problems with USB driver. So here is the solution. First unload the old module
sudo rmmod rndis_host cdc_ether usbnet |
sudo rmmod rndis_host cdc_ether usbnet
Now, remove it
sudo rm /lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel/drivers/net/usb/{rndis_host,cdc_ether,usbnet}.ko |
sudo rm /lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel/drivers/net/usb/{rndis_host,cdc_ether,usbnet}.ko
Compile the new USB driver: usb-rndis-source and cdbs
sudo apt-get install usb-rndis-source cdbs
sudo module-assistant auto-install usb-rndis |
sudo apt-get install usb-rndis-source cdbs
sudo module-assistant auto-install usb-rndis
Fixed! Now back to SynCE story… We need to install several libraries which are odccm, librra0-tools and librapi2-tools
sudo apt-get install odccm librra0-tools librapi2-tools |
sudo apt-get install odccm librra0-tools librapi2-tools
Now connect your device and run the following command
IF you can see the lisft of files on your device, your device is successfully connected to your Linux machine.
BUT if it returns you the following error message, you need to install SynCE-GNOME or SynCE-KPM to provide a password prompt on device connect.
. WARNING **: synce_info_from_odccm: Failed to get a connection for <device_name>: Not authenticated, you need to call !ProvidePassword with the correct password. pls: Could not find configuration at path '(Default)' |
. WARNING **: synce_info_from_odccm: Failed to get a connection for <device_name>: Not authenticated, you need to call !ProvidePassword with the correct password. pls: Could not find configuration at path '(Default)'
To start sync your device, you need OpenSync.
sudo apt-get install multisync-tools opensync-plugin-evolution opensync-plugin-synce |
sudo apt-get install multisync-tools opensync-plugin-evolution opensync-plugin-synce
Wee..! Your device is ready to sync. Please refer to OpenSync page for tutorial on how to use OpenSync
For the official guide, please visit http://www.synce.org



